Last modified:
In the mathematical sense, a “term” allows you to define custom data points at the system Level using your own formula, which is evaluated for the variables used for every available timestamp.
The Term editor in VCOM allows you to process measured data from your system and generate key performance indicators. Terms are integral to charts, simulations, KPIs, evaluations, and certain portlets.
Example
You can use terms to calculate the average for several sensors or to define the parameters to determine the total energy generated (E_Z_EVU).
Create a term
Prerequisites
-
You belong to the user group technician, operations, or administrator. See User groups.
-
At System level , go to



-
If necessary, view the available datapoints (= variables) and corresponding terms, and select relevant devices in the

-
Select

-
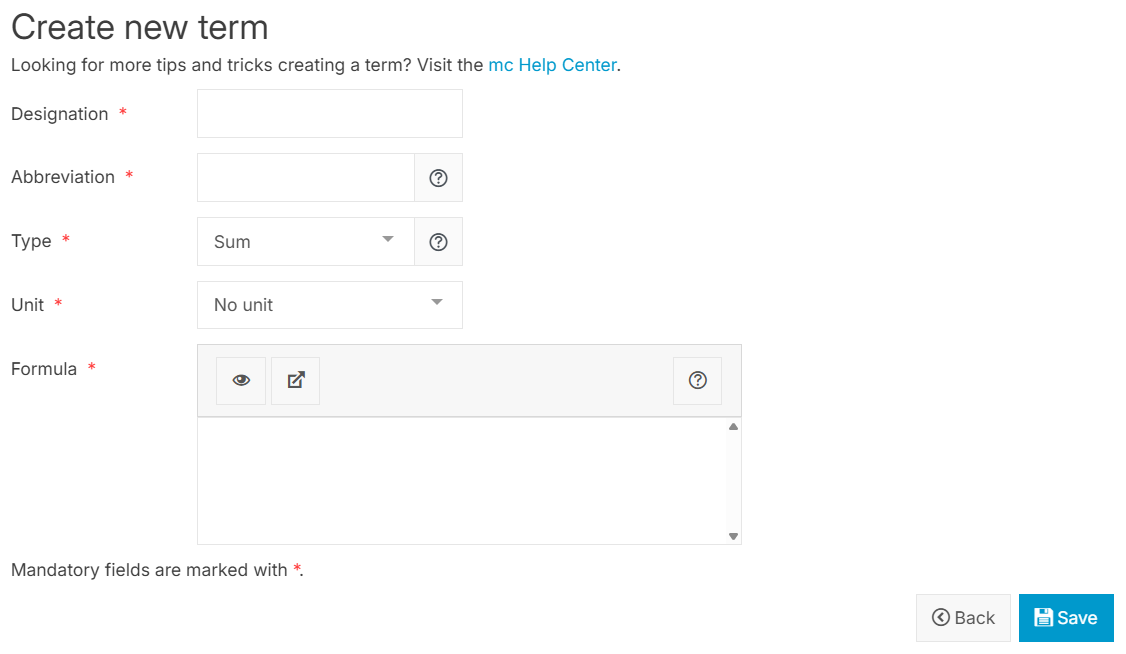
Define term properties:
-
Designation: Give your term a designation. This is a user-friendly name that will later be visible in graphs and reports. The designation is not translated into other languages.
-
Abbreviation: Give your term an abbreviation. This defines how the results of this term can be referenced in other terms and through the VCOM API. If possible, use the defined abbreviations. See Terms abbreviations with a special meaning.
-
Type (Aggregation): Select how the values that this term yields should be aggregated. Currently, there are two options:
-
Sum: Results are summed up over time (e.g. energy values).
-
Average: Results are averaged over time (e.g. temperature values).
-
-
Unit: Select the unit to be displayed in charts and reports.
Important: If the unitW/m²is used, the type Average should be selected, as for time intervals greater than one hour, the aggregation will automatically switch to the unitWh/m². -
Formula: Define a formula for your term, consisting of variables, numbers, operators, and simple or complex functions. See also Formulas. If necessary, read the


-
-
Select

The term appears in the list of terms and can now be applied throughout VCOM, for example, in the Power flow portlet and Charts.
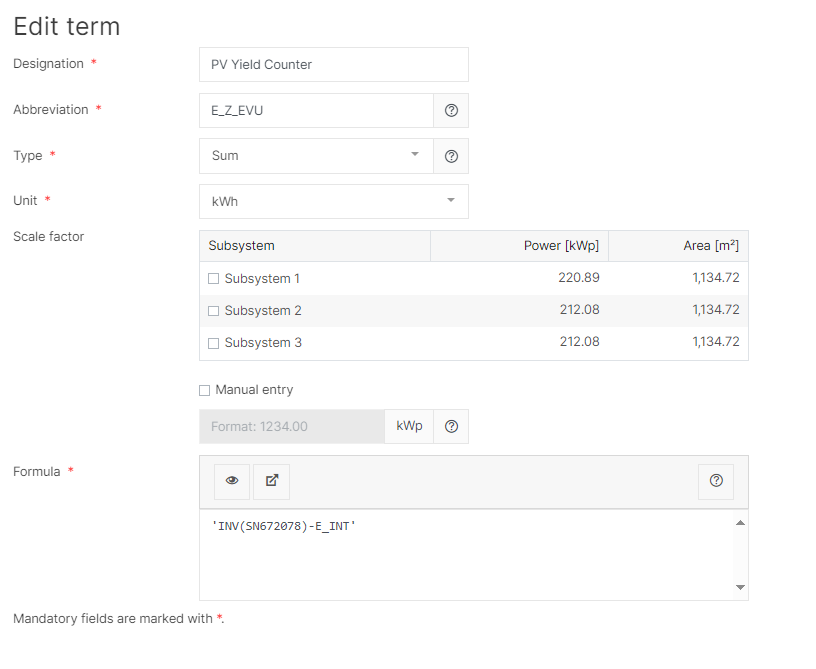
Example
In the example below, the datapoint E_Z_EVU is defined as the energy sum of the inverters.
-



Recalculation of terms
If you change a term, you may need to recalculate all terms for previous periods.
Caution
Recalculation of terms will overwrite previous values.
-
You belong to the user group technician, operations, or administrator. See User groups.
-
At System level , go to



-
Select

-
Enter the period for which you want to re-calculate all newly created terms. If the recalculation period exceeds 1 year, you must perform another recalculation.
-
Select

All terms are now recalculated for the selected period,, and charts will display the new values.
Abbreviations with a special meaning
You can find a full list of all abbreviations under ![]()
|
Abbreviation |
Required unit |
Description |
Used in VCOM |
Further details |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
E_Z_EVU |
kWh |
Actual generated energy per interval for the whole system, including manual meter entries. |
|
VCOM’s default definiton is ‘E_INT', which includes all inverters. Redefine the formula for this data point to suit your needs and your system setup. |
|
E_Z_x (x = 1...99) |
kWh |
Other actual generated energy per interval measurements, for example for subsystems. |
|
Create further E_Z_x terms on your own and based on your sytem setup. |
|
E_MESS |
kWh |
Actual generated energy per interval for the whole system, excluding manual meter entries. |
|
You can not redefine the formula for this data point. |
|
G_M0 |
W/m² |
Plane of array irradiance/POAI |
|
If your system has multiple irradiance sensors, select the ones you want to include in the formula for G_M0 at System level , under Caution Do not use satellite irradiance data points to define G_M0. Satellite date is available only with a delay and only on an hourly basis. This would lead to irregularities in KPIs, simulation, and therefore various charts. |
|
G_Mx (x = 1…99) |
W/m² |
Other plane of array irradiance/POAI measurements |
|
Create further G_Mx terms on your own and based on your sytem setup. |
|
G_H0 |
W/m² |
Global horizontal irradiance/GHI |
|
|
|
G_Hx (x = 1...99) |
W/m² |
Other global horizontal irradiance/GHI measurements |
|
Create further G_Hx terms on your own and based on your sytem setup. |
|
M_AC_E_EXP |
kWh |
Energy grid export |
For creating these terms, see Self-consumption terms. |
|
|
M_AC_E_IMP |
kWh |
Energy grid import |
||
|
M_AC_E_OWN |
kWh |
Energy self-consumption |
||
|
M_AC_E_CON |
kWh |
Energy total consumption |
||
|
B_E_DISCHARGE |
kWh |
Battery discharging |
||
|
B_E_CHARGE |
kWh |
Battery charging |
||
|
PF_P_GRID |
W |
Import/export power |
Create the respective terms by configuring the portlet when you first add it to a tab. |
|
|
PF_P_CON |
W |
Consumption power |
||
|
PF_P_BAT |
W |
Battery power |
||
|
T_M0 |
°C |
Module temperature per interval for the whole system |
|
|
|
T_Mx (x = 1...99) |
°C |
Other module temperature measurements per interval |
|
Create further T_Mx terms on your own and based on your sytem setup. |
|
T_Ux (x = 0...99) |
°C |
Ambient temperature measurements |
|
Create further T_Ux terms on your own and based on your sytem setup. |
|
W_Vx (x = 0…99) |
m/s |
Wind speed measurements |
|
Create further W_Vx terms on your own and based on your sytem setup. |
|
W_Dx (x = 0…99) |
° |
Wind direction measurements |
|
Create further W_Dx terms on your own and based on your sytem setup. |
Formulas
Variables and data source
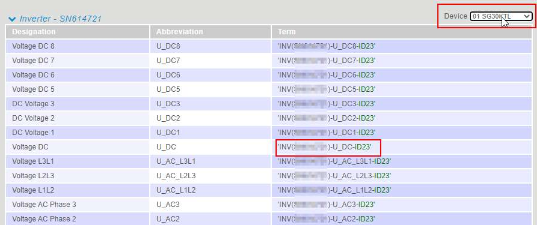
You must specify at least one variable for each formula otherwise nothing will be calculated. VCOM provides you with an overview of the available datapoints (= variables) and the corresponding terms for your system. For this, select ![]()
'). Any configured device can be selected separately via the dropdown menu. If no device is selected, the sum of all devices will be taken.
Notes
-
The result of the term is not tied to a specific device; even if it uses the values from one device, it applies to the entire system and is not associated with any particular device.
-
For the sake of simplicity, the example used below will not use variables and use
NULLto represent a null-value returned by a variable or calculation.
Numbers
In addition to variables, numbers can be used. Both , and . can be used as a decimal separator. Thousands separators and scientific notation are not supported.
Operators
To combine multiple variables (and numbers), various operators are available. In general, all operators will yield null if any of the operands are null, the only exception of that rule being ??. The precedence describes the order of calculation, with higher precedence evaluated before lower precedence
Functions
In addition to operators, functions can greatly reduce the complexity of formulas. Functions calls consist of a function identifier, followed by a list of parameters (separated by ; ) in parenthesis ( ). Calling functions with fewer/more parameters than required is an error.