Active power (with Hybrid EMS)
Last modified:
Active power overview
Under Power control > Active power, you can configure parameters related to active power control. Here is an overview of the user interface for this:
.png?inst-v=05a6ccb9-7ad8-4cdf-9b8b-ba33c3614d94)
.png?inst-v=05a6ccb9-7ad8-4cdf-9b8b-ba33c3614d94)
Active power overview
Item | Name | Details |
|---|---|---|
1 | Active power control toggle | Activate the toggle ONLY after you have fully configured your power control setup |
2 | Extended settings icon | Configure system behavior, including controller sampling time (default value: 500 ms), setpoint reference, and control criterion |
3 | Basic settings |
|
4 | Operation mode |
|
5 | Fail-safe operation | Configure fail-safe behavior in case of communication loss. See Fail-safe operation (with Hybrid EMS). |
6 | Automatic grid disconnection | Activate the automatic grid disconnection feature (license required). See Zero feed-in and automatic grid disconnection (with Hybrid EMS). |
7 | Ramp rate limiter | Configure ramp rate limiter. |
8 | Frequency dependent control | Configure frequency control. |
Description of functions
PV self-consumption
PV self-consumption is only available if both PV and Battery are selected under Plant data (with Hybrid EMS). The hybrid system is controlled such that all available solar power is used for self-consumption to cover the local load. Any excess solar energy is used to charge the battery. Power is only fed into the grid when the battery is fully charged. If solar energy generation is not sufficient to cover the local load, the battery discharges the stored energy. In this mode, the PV system is never curtailed.

PV self-consumption
Setpoint command
Setpoint command is available in all system configurations: PV only, battery only, or PV + battery. In this mode, the active power is controlled according to a setpoint at the grid connection point.
The interface to transmit the setpoint can be selected under Setpoint command method. The setpoint command can be set via digital inputs, analog inputs, Modbus, or it can be locally configured in the user interface. These methods are mutually exclusive—only one can be active at a time. A method switch can be configured to change between them.
Setpoint commands are typically sent by the grid operator to curtail the system. In some cases, a third party, such as an energy trader, may also control the system. This requires the Remote Power Control (RPC) license. See Remote power control (with Hybrid EMS).
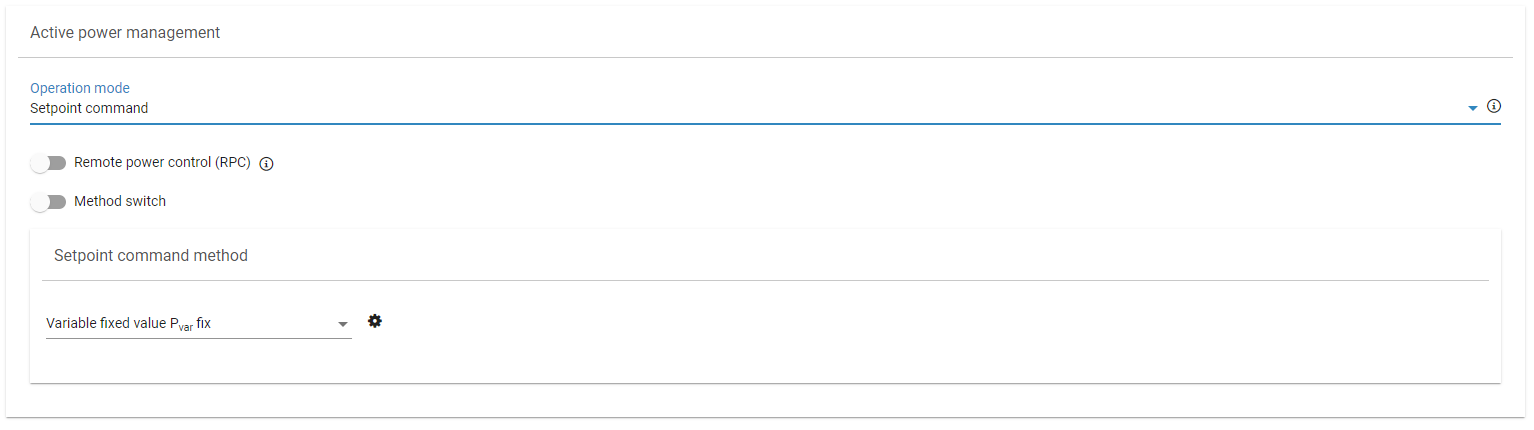
Setpoint command method
When both PV and battery are selected, priority is given to the PV system to adhere to the setpoint. As a result, the PV system is curtailed only if the battery cannot absorb the energy required to meet the setpoint.
Example: Zero-feed in with a setpoint of 0 kW:
All available solar power is used for self-consumption. When more solar power is produced than can be consumed locally, as much energy as possible is stored in the battery system. Once the battery system is fully charged, excess solar power is curtailed so that no power is fed into the grid. The battery system begins discharging as soon as solar generation can no longer cover local consumption.
Band shaving
The hybrid system operates within a predefined band at the grid connection point. When not enough PV power is available and the lower threshold of the band is reached, the battery starts discharging to avoid peak loads. If the upper threshold is reached, the battery starts charging. If the battery is fully charged, the PV system is curtailed so that it does not exceed the band.

Band shaving
State of charge limitation
You can prevent the battery from fully discharging and/or overcharging by activating the State of charge limitation function. Here you can set the following:
Minimum state of charge SOC)
Maximum state of charge (SOC)
The battery will stop charging once the maximum SOC is reached and will stop discharging once the minimum SOC is reached.
The overall state of charge of all batteries is calculated based on the single capacities of the batteries and their current state of charge.
Note
If several batteries are connected, the state of charge limitation only applies to the overall state of charge of all batteries.
Example
Battery 1: max capacity 500 kWh, SOC = 40 %
Battery 2: max capacity 200 kWh, SOC = 30 %
The overall state of charge is (40 % * 500 kWh + 30% * 200 kWh) / (500+200) kWh = 37.14%.
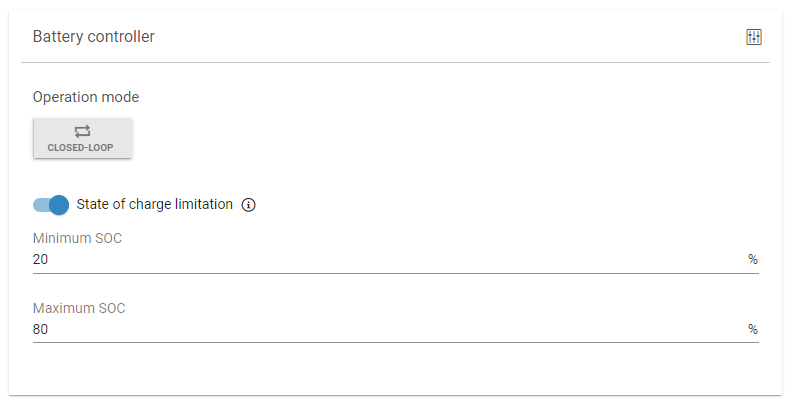
State of charge limitation
.png)