Frequency control modes (with Hybrid EMS)
Last modified:
About frequency-dependent control
All countries have a standard grid frequency, for example, 50 Hz in Europe, and it is essential to maintain the frequency to prevent blackouts and damage. The grid code of each country requires power-generating systems to apply frequency control during inadmissible system frequency changes. Depending on the requirements, this can be carried out by the inverters or a plant controller such as the blue’Log.
The blue’Log interface allows you to regulate the active power output in three different modes:
Limited frequency sensitive mode - underfrequency (LFSM-U)
Underfrequency occurs when the frequency of the electrical grid falls below the nominal operating frequency. To correct this, the active power output of the system is increased according to a characteristic curve P(f) until the grid frequency returns to the permissible range.
When setting LFSM-U on the blue’Log, consider the following:
Each parameter is described in the
 Info buttons next to each parameter
Info buttons next to each parameterRefer to your local grid operator requirements when setting the parameters
You can configure additional frequency bands/slopes if necessary
You can prioritize the grid operator setpoint via the Prioritising grid operator setpoint toggle. See Prioritization between different control modes (with Hybrid EMS).
Limited frequency sensitive mode - overfrequency (LFSM-O)
Overfrequency occurs when the frequency of the electrical grid exceeds the nominal operating frequency. To correct this, the active power output of the system is limited according to a characteristic curve P(f) until the system frequency returns to the permissible range.
When setting LFSM-O on the blue’Log, consider the following:
Each parameter is described in the
 Info buttons next to each parameter
Info buttons next to each parameterRefer to your local grid operator requirements when setting the parameters
You can configure additional frequency bands/slopes if necessary
You can prioritize the grid operator setpoint via the Prioritising grid operator setpoint toggle. See Prioritization between different control modes (with Hybrid EMS).
Frequency sensitive mode (FSM)
In this mode, the active power is also adjusted according to a defined P(f) curve to provide the ancillary service frequency containment reserves (FCR, also known as primary control reserves). Thus, FSM is only relevant if your system participates in the electricity balancing market. Compared to the LFSM-O and LFSM-U modes, FSM mode is usually active during smaller frequency deviations. In case of overlap LFSM-O and LFSM-U have priority over FSM.
When setting FSM on the blue’Log, consider the following:
Each parameter is described in the
 Info buttons next to each parameter
Info buttons next to each parameterRefer to your local grid operator requirements when setting the parameters
Some parameters can be configured via Modbus. The Modbus Power Control license is required for this. Refer to the data sheet for the relevant addresses: Downloads - meteocontrol GmbH.
Activate FSM via an external signal via the Activate FSM via Modbus toggle.
Set the active power range via the Set active power range via Modbus toggle.
FSM working principle and example
The example below illustrates how FSM mode works. The following settings are used:
Active power range |ΔP1|/Pmax= 6%
Frequency droop sf = 5%
Deadband ΔfDB = 50 mHz
Reference active power Pref = Momentary active power Pmom
Nominal system frequency fn = 50 Hz
Base value = Momentary active power Pmom (Note: the option to choose the base value is only available if the Remote Power Control license is installed)
These settings result in the following P(f) characteristic curve:
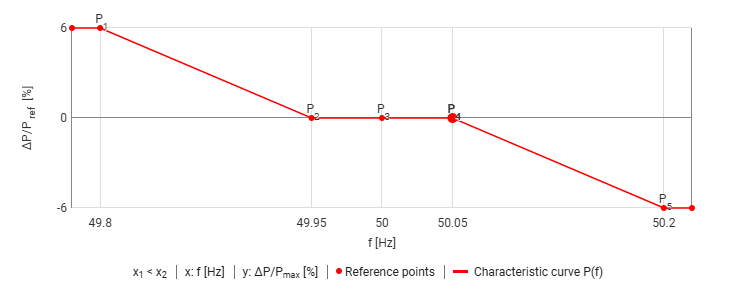
Example: P(f) characteristic curve with FSM
In FSM mode, the frequency is continuously measured and the active power is adjusted according to the defined P(f) characteristic curve
Frequency within deadband ΔfDB (f > 49.95 and f < 50.05 Hz): No active power adjustment
Frequency outside deadband ΔfDB (f < 49,95 or f > 50,05 Hz): Active power adjustment according to the following formula:
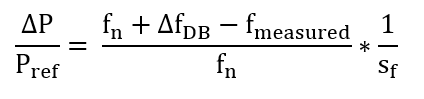
With a measured frequency fmeasured = 50.2 Hz and the above settings, the resulting relative active power change ΔP/Pref equals -6%.
The absolute active power change ΔP depends on the set reference active power Pref.
In the example here, Pref equals Pmom (e.g. 3,5 MW). Thus, the absolute active power change ΔP equals -210 kW.
The absolute active power change ΔP is added to the base value Pbase to obtain the final setpoint of this mode.
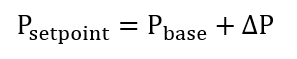
The base value Pbase can only be selected if the Remote Power Control license is installed.
If the Remote Power Control license is not installed, the base value Pbase always corresponds to Pmom.
Setting the base value to PRPC also enables energy traders to adjust the active power output during FSM events.
Activate frequency-dependent control
Prerequisites
Only the user group Service can make changes. See Users
Meter/power analyzer is compatible with blue'Log. See Compatibility Check
Meter/power analyzer fulfills the measurement requirements for frequency-dependent control
Example: Your grid code requires the frequency to be measured with a certain accuracyFrequency-dependent control is only available for the operation mode Setpoint command.
For configuration assistance, we recommend our project-specific controller tuning services. See Downloads - meteocontrol GmbH.
Steps
Go to Power control > Active power > Active power management > Select Setpoint command.
Go to Options and activate the Frequency dependent control toggle.
Activate the toggle for the desired control mode and select the Gear icon to configure the parameters.
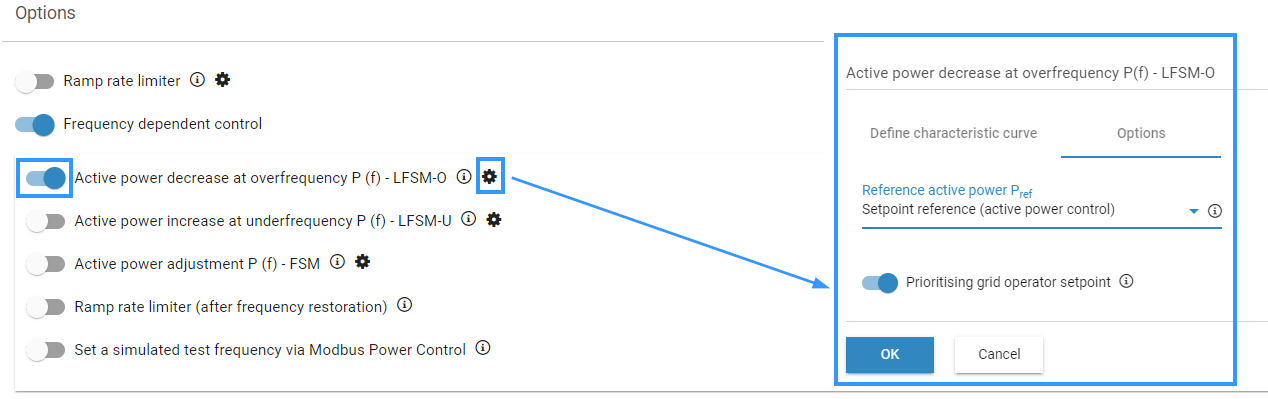
Frequency-dependent control: example configuration with LFSM-O
Set a simulated test frequency via Modbus Power Control
Many markets require verification of the settings, for example during the commissioning process.
To test your frequency-dependent control settings, activate the Set a simulated test frequency via Modbus Power Control toggle. The Modbus Power Control license is required for this.
For more on verification and compliance, see the data sheet for Grid code compliance engineering services: Downloads - meteocontrol GmbH.
Set a ramp rate limiter (after frequency restoration)
If the frequency event ends and the frequency is restored, a ramp rate limiter can be applied to the transition to normal operation.
Example: power was reduced to 500 kW during the frequency event, but the plant can deliver 800 kW after the frequency event ends, and no power limitations are present. In this scenario, if the ramp rate limiter is activated after frequency restoration, the power does not immediately return to maximum power (800 kW) but has a configurable rate of change.
This function applies only after LFSM-U and LFSM-O events and cannot be set if FSM is activated.
.png)