Last modified:
About virtual meters
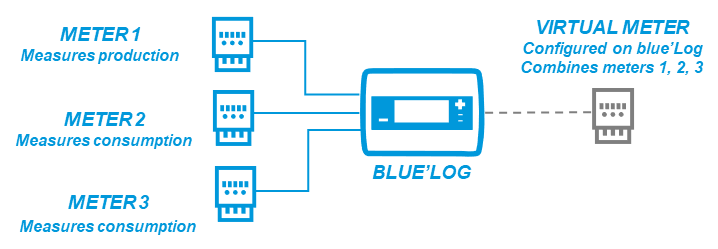
On the blue’Log, a virtual meter is a single virtual device designed to combine real meters into a single meter for monitoring and power control purposes (for example, in zero feed-in scenarios). In some cases, the virtual meter feature replaces the need for a PLC.
-
You can only configure one virtual meter per blue’Log.
-
A virtual meter also counts as a device in the maximum device count for the blue'Log. Example: 10 real meters + 1 virtual meter = 11 devices.
-
The algorithm behind the calculation of each parameter sums up the meter values and creates average values (where appropriate).
-
Firmware 26.0.6 and above: If one or more real meters have the option "phase-related control", the virtual meter will also have this feature.
-
The virtual meter will be impacted if one of the real meters is unavailable. In this case, an error message will appear on the blue’Log.
Virtual meter and failsafe operation
-
If a real meter is not sending values due to a communication loss, it is excluded from the calculation to avoid incorrect values. In this case, the blue’Log switches to fail-safe operation.
-
Failsafe mode is not triggered by the following if the real meter:
-
Sends incorrect values
-
Sends corrupt values, such as fractions, negative values, or extremely high values
-
Omits a single value, such as P or Q
-
Add a virtual meter
Prerequisites
-
At least two meters are configured and available
-
Firmware 25.0.13 or higher
-
To use a meter as a source for power control in a master-slave setup:
-
The real meters must be connected to the Master blue'Log.
-
The virtual meter must be configured on the Master blue'Log.
-
Steps
-
Go to Devices > Meters > Virtual meter > Manage virtual meter.
-
Select the meters to combine into a virtual meter. Click the Plus icon to add additional meters.
-
Enter a name for the virtual meter.
-
Select the Reference arrow system.
-
Select the device role. For power control, select Feed in and import.
-
Select Save.
-
The device will appear under Installed devices.
Example
For power control, feed-in is measured as positive, and self-consumption is measured as negative. The virtual meter allows the blue'Log to calculate multiple meter values. These measured values are the basis for power control with the blue'Log. The graphic below shows how a virtual meter is used for power control calculations:
Note
Cos phi (also known as cos φ or power factor) is a calculated value.
When multiple real meters are combined into a virtual meter, the cos phi value is calculated based on the following formula:
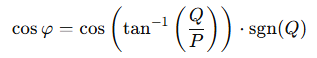
Variables
-
P is the measured active power sum of all phases
-
Q is the measured reactive power sum of all phases
-
tan-1 represents the arctangent function
-
sgn(Q) represents the sign of Q, so if Q is underexcited it is -1, otherwise it is 1
Any measured values from the individual meters are ignored.