Operating data (without Hybrid EMS)
Last modified:
Under Power control > Operating data, you can view a summary of system data related to power control functions. This overview is divided into several sections, which are explained in more detail below.
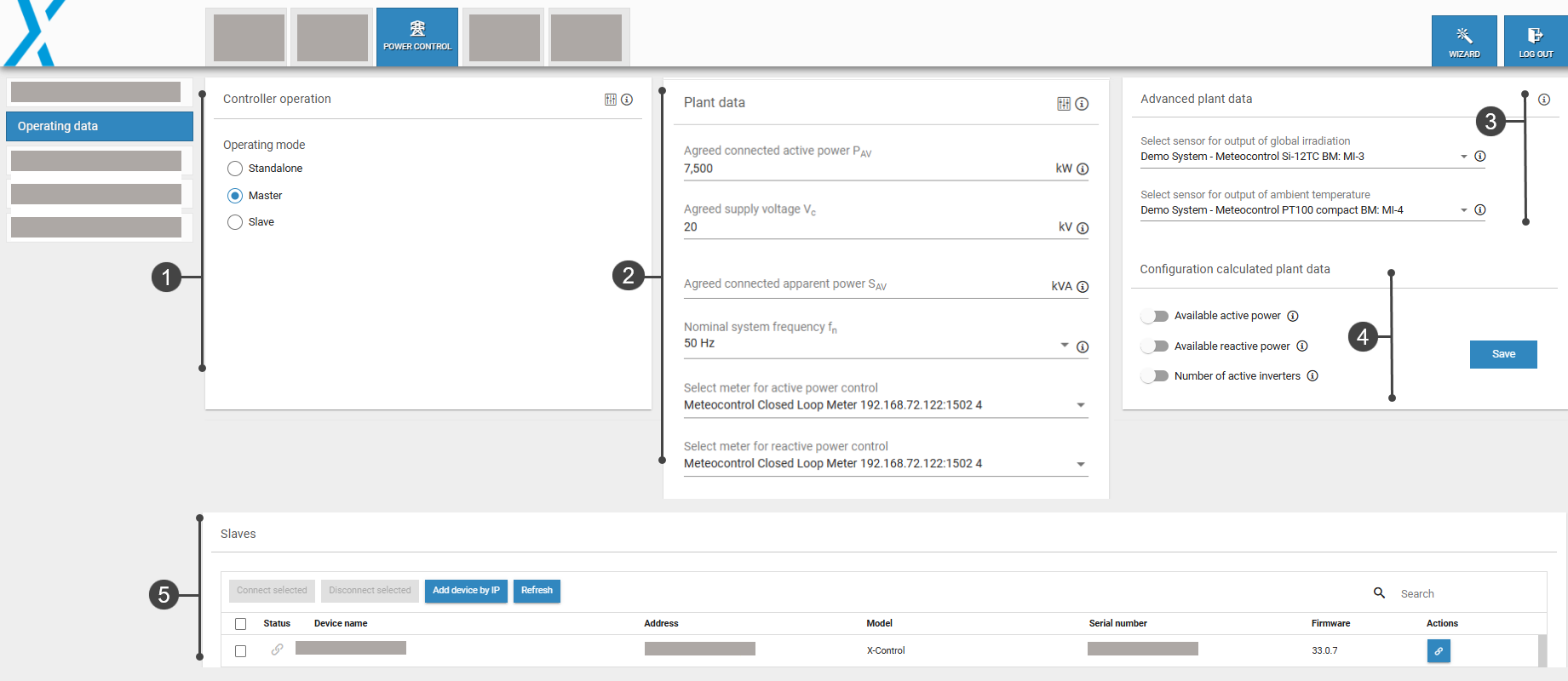
Operating data overview
1. Controller operation
The blue'Log can be operated in three different modes:
Standalone: Only one blue'Log is used for controlling your system
Master: Several blue'Logs are required for large-scale control over your system, with the devices running in master-slave operation. The master blue'Log XC sends signals to a slave blue'Log XM.
Slave: A slave blue'Log XM receives signals from the master blue'Log XC.
For details about each operating mode, see Controller operation modes: standalone, master, slave.
2. Plant data
You can configure the electrical characteristics of your plant under Plant data. All settings are mandatory except for the ![]() Extended settings.
Extended settings.
Parameters
Select a parameter to view more details.
Meter
Select the relevant meters for active and reactive power. The measured values of both meters will be displayed under Power control > Overview. See also Mixed installations/plants.
For open-loop operation, a meter is not mandatory. For more information on open/closed loop, see Closed loop vs open loop control (without Hybrid EMS).
3. Advanced plant data
Under Advanced plant data, you can configure irradiance and temperature sensors to make their data points accessible via Modbus.
Prerequisites
Sensors must be configured under Devices > Sensors.
The Modbus Power Control or Remote Power Control license is required to access these data points. See License and data sheets: Downloads - meteocontrol GmbH
Configure sensor for output of global irradiation
Here you can assign an irradiance sensor to a master or slave device.
The number of sensors varies depending on the operating mode of the controller (standalone, master, slave).
 Gear icon: If a device has several irradiance sensors, select the measured value to be forwarded via Modbus, e.g. irradiance W/m2.
Gear icon: If a device has several irradiance sensors, select the measured value to be forwarded via Modbus, e.g. irradiance W/m2.Advanced settings: Modbus assumes that irradiance sensors are mounted horizontally. If the sensor is mounted at an incline (for example, on a PV module), activate the toggle and enter the inclination angle (in degrees) of the sensor.
Configure sensor for output of ambient temperature
Here you can assign a temperature sensor to a master or slave device.
 Gear icon: If a device has multiple temperature sensors, select the measured value to be forwarded via Modbus.
Gear icon: If a device has multiple temperature sensors, select the measured value to be forwarded via Modbus.
4. Calculated plant data
Grid operators, plant operators, direct marketers, or balancing service providers want to know the potential production of a PV plant.
Grid operators want to know a plant’s reactive power capability to estimate its contribution to voltage stability.
The values Available active power and Available reactive power can be read via the Modbus interfaces Modbus Power Control and Remote Power Control.
See Calculated plant data (without Hybrid EMS) for further details.
5. Slaves
The Slaves area shows all available devices that can be connected as slave devices.
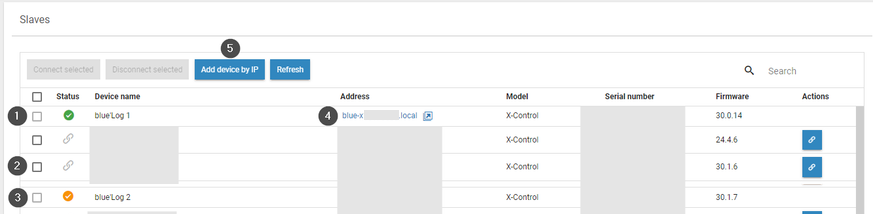
Item | Name | Details |
|---|---|---|
1 | Green check mark | The slave is connected to this device |
2 | Chain icon | Connect a device as a slave to this device |
3 | Yellow check mark | The slave is connected to another device |
4 | Arrow icon | Access the web interface for this slave device |
5 | Add device by IP | Manually add a device using its IP address |
.png)